The global encoders market is undergoing a significant transformation as it rides the wave of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing. As businesses across the globe adopt automation, digitalization, and intelligent machinery to remain competitive, encoders—devices that translate motion into digital signals—are emerging as critical components in modern industrial ecosystems. These small but powerful devices are playing a pivotal role in enabling the accuracy, precision, and connectivity that smart systems demand.
The Role of Encoders in Smart Manufacturing
Encoders are essential for measuring position, speed, rotation, and direction in mechanical systems. They are widely used in robotics, conveyor systems, CNC machinery, elevators, medical imaging devices, and even in autonomous vehicles. In the context of smart manufacturing, encoders provide the feedback necessary for machines to operate with pinpoint accuracy and real-time responsiveness. This enables automated systems to self-correct, optimize performance, and communicate seamlessly with other parts of a production line.
Smart factories rely on interconnected machines that can collect and exchange data through industrial networks. Encoders are integral to this connectivity. They enable machines to monitor and report on their own operation, which in turn supports advanced capabilities such as predictive maintenance, adaptive control, and real-time quality monitoring. Without the precise, reliable feedback encoders provide, the level of automation and intelligence required in modern production environments would not be possible.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=14566162
Industry 4.0 as a Catalyst for Market Growth
Industry 4.0 is reshaping global manufacturing by integrating cyber-physical systems, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). In this digital-first industrial age, the demand for smart sensors and feedback devices is increasing at an unprecedented rate. Encoders, both rotary and linear, form the backbone of many of these technologies by offering accurate motion control and positioning in a wide range of applications.
As companies upgrade legacy systems and adopt new technologies to remain competitive, encoder technology is being integrated into every aspect of industrial automation. From robotic arms in assembly lines to automated guided vehicles (AGVs) in logistics, encoders ensure precise operation. The need for real-time data, combined with tighter tolerances and increased machine autonomy, is pushing manufacturers to adopt high-performance encoder solutions capable of operating under harsh industrial conditions.
Market Dynamics and Regional Insights
The encoders market is experiencing robust growth across multiple regions, with Asia-Pacific leading in terms of both production and consumption. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in factory automation, robotics, and smart infrastructure, making the region the fastest-growing market. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are spearheading innovation in encoder design, with an emphasis on high-end applications such as aerospace, automotive, and advanced healthcare systems.
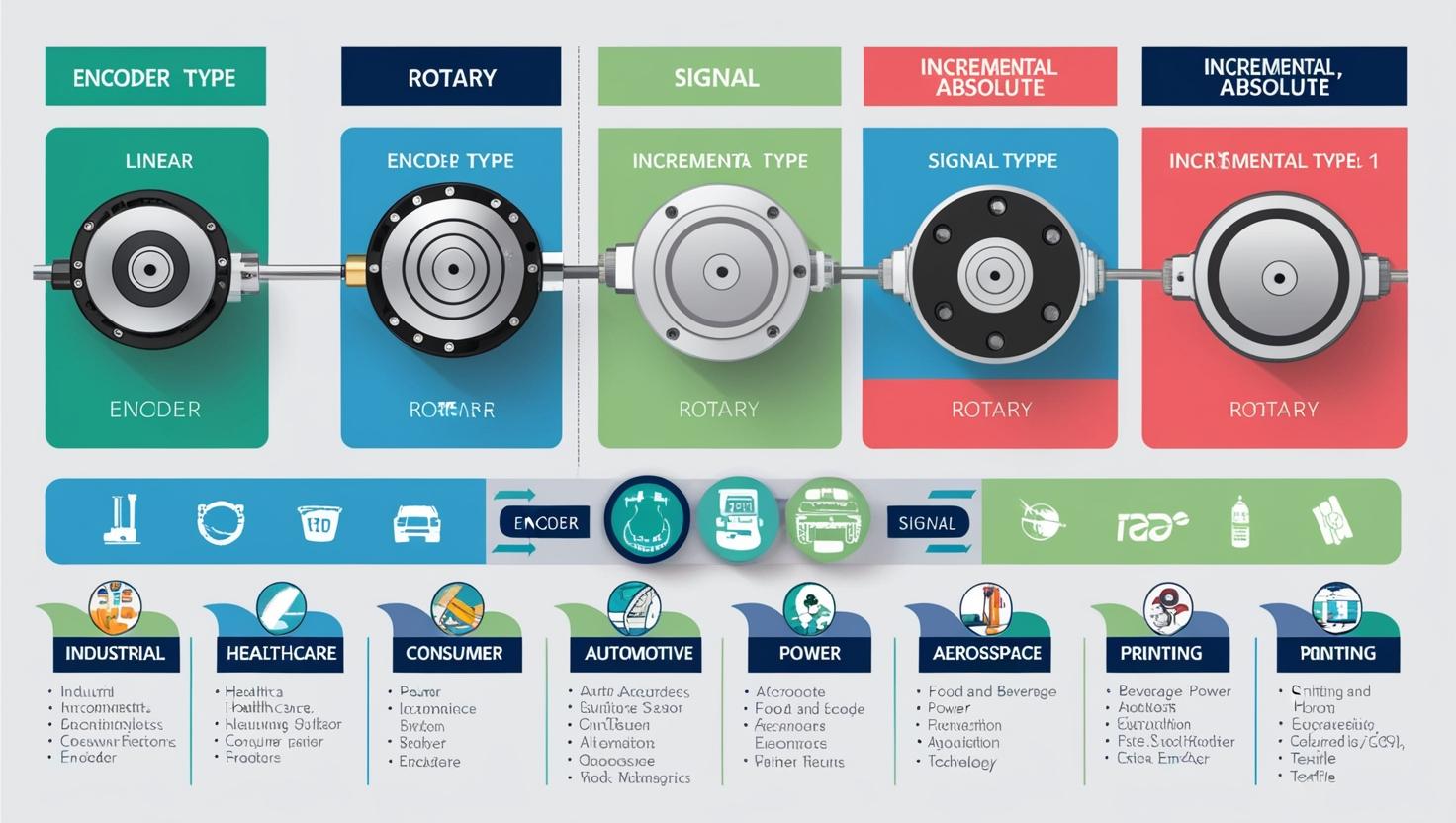
Rotary encoders continue to dominate the market due to their versatility and widespread use in motion control systems. However, linear encoders are gaining popularity in precision manufacturing applications where exact measurements are critical. Optical encoders remain the preferred choice in environments requiring high resolution and accuracy, while magnetic encoders are increasingly adopted in applications that demand durability and resistance to contaminants such as dust, oil, and moisture.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The evolution of encoder technology is closely tied to advances in electronics, materials science, and software. One major trend is the miniaturization of encoders. As robotics and automated devices become smaller and more sophisticated, encoders must follow suit without compromising on performance. Manufacturers are developing ultra-compact encoders that can fit into tight spaces while maintaining high levels of accuracy.
Another significant innovation is the integration of encoders with wireless communication and IoT platforms. Wireless encoders allow for greater flexibility in system design and enable remote monitoring, reducing the need for physical maintenance. Some modern encoders are now equipped with self-diagnostic capabilities, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Furthermore, AI-enhanced encoders can now adapt to changing conditions, auto-calibrate, and provide deeper insights into system performance.
Energy efficiency and sustainability are also becoming priorities for encoder manufacturers. As environmental regulations tighten and sustainability becomes a core focus for industrial operations, there is growing demand for encoders made from recyclable materials and designed for lower energy consumption over their lifecycle.
Competitive Landscape and Future Outlook
The encoders market is highly competitive, with global players such as Heidenhain, Renishaw, Rockwell Automation, Siemens, Honeywell, and Baumer leading the charge. These companies are continuously investing in R&D to develop next-generation encoder solutions that offer higher resolution, enhanced durability, and better integration with smart systems. In addition to large corporations, many startups and mid-sized firms are carving out niches by offering specialized encoder solutions for emerging industries such as renewable energy, electric vehicles, and medical robotics.
Looking ahead, the future of the encoders market appears promising. As more industries embrace automation and digital transformation, the demand for encoders will continue to rise. The expansion of smart cities, the electrification of vehicles, the proliferation of robotics, and the growth of precision agriculture are just a few of the sectors poised to fuel this growth.
In conclusion, encoders are no longer just peripheral components in mechanical systems—they are central to the intelligence, precision, and connectivity that define modern industry. With Industry 4.0 accelerating the pace of innovation and adoption, the encoders market is well-positioned to see sustained growth in the coming decade.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – Encoders Market
1. What is an encoder, and why is it important in industrial applications?
An encoder is an electromechanical device that converts motion (such as rotation or linear movement) into a digital signal, which can be interpreted by a control system. In industrial applications, encoders are crucial for providing feedback on position, speed, and direction, enabling precise control of machinery, automation systems, and robotics.
2. What are the main types of encoders available in the market?
The most common types of encoders are:
- Rotary Encoders: Measure angular motion or position.
- Linear Encoders: Measure straight-line movement.
- Incremental Encoders: Provide relative position changes.
- Absolute Encoders: Provide a unique position value for each shaft angle or position.
- Optical Encoders: Use light to detect motion (high precision).
- Magnetic Encoders: Use magnetic fields (more rugged and durable).
3. What is driving the growth of the global encoders market?
The market is primarily driven by the rise of Industry 4.0, increased demand for automation, robotics, and smart manufacturing systems. Other contributing factors include the expansion of the automotive, consumer electronics, healthcare, and aerospace sectors, all of which rely heavily on precision motion control.
4. How does Industry 4.0 impact the encoder market?
Industry 4.0 emphasizes data-driven manufacturing, smart sensors, machine learning, and system interconnectivity. Encoders enable machines to communicate real-time data about motion and performance, supporting functions such as predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and autonomous operation. This makes encoders essential to the digital transformation of industries.
