Artificial Intelligence (AI) has profoundly transformed the field of computer vision, enabling machines to interpret and understand visual data with remarkable accuracy. From facial recognition and object detection to medical diagnostics and industrial automation, AI-powered computer vision is revolutionizing how businesses, governments, and consumers interact with technology. As the volume of visual data continues to explode, the integration of AI in computer vision is emerging as a key driver of innovation, automation, and competitive advantage across industries.
The Evolution of Computer Vision with AI
Traditional computer vision relied heavily on manually coded rules to interpret visual input, which made systems brittle and limited in application. The introduction of AI—particularly deep learning—marked a significant leap forward. With convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and other machine learning algorithms, computer vision systems can now “learn” from vast datasets, identifying patterns and making predictions with minimal human intervention.
This shift has enabled a new generation of vision systems that are not only more accurate but also adaptive and scalable. AI-driven computer vision systems can now recognize faces, interpret traffic signs, detect anomalies in manufacturing lines, and even assist in surgical procedures—all with a level of precision previously thought unattainable.
Core Capabilities of AI-Powered Computer Vision
AI enhances computer vision in several key areas. Object detection and image classification allow systems to identify and label objects within images or video streams. Image segmentation enables the precise delineation of objects from the background, which is critical in fields like autonomous driving and medical imaging. Optical character recognition (OCR) can extract and analyze text from images or documents. Beyond static images, AI can also track objects in real-time video, enabling applications in security surveillance, sports analytics, and robotics.
Furthermore, AI models are increasingly being trained using transfer learning and unsupervised learning techniques, reducing the dependence on large, labeled datasets. This makes it easier and faster to deploy custom vision solutions in specialized domains.
Download PDF Brochure @
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=141658064
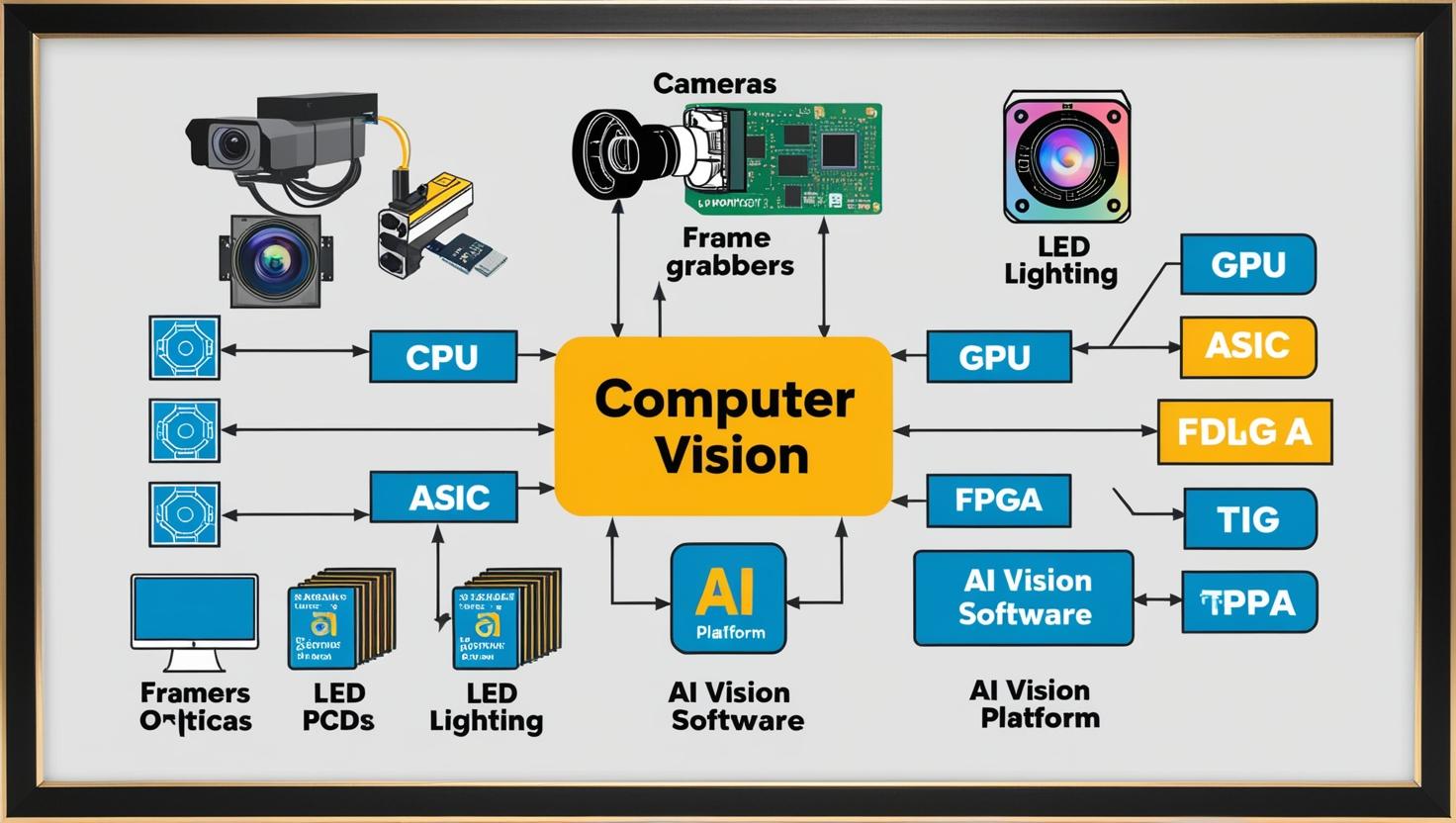
Industrial and Commercial Applications
In manufacturing, AI-based computer vision is driving smart factories by enabling predictive maintenance, quality assurance, and process optimization. Defect detection systems can now identify minute anomalies on production lines in real time, reducing waste and ensuring product consistency.
In healthcare, computer vision assists with early diagnosis of diseases through the analysis of medical images like MRIs, X-rays, and CT scans. Radiologists are now supported by AI tools that highlight suspicious areas, improving diagnostic accuracy and efficiency.
Retail and e-commerce industries are leveraging AI for customer behavior analysis, visual search, and inventory management. Self-checkout systems and smart shelves rely on computer vision to recognize products and transactions without human input.
In transportation and logistics, AI-driven vision systems are used for vehicle recognition, traffic monitoring, and autonomous driving. Companies like Tesla and Waymo rely heavily on vision-based AI systems to interpret the environment and make driving decisions.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
One of the most promising trends is the rise of edge AI, where computer vision models are deployed directly on devices such as drones, smartphones, and industrial cameras. This reduces latency, enhances privacy, and allows real-time processing without relying on cloud infrastructure.
Another major development is the integration of multimodal AI, which combines computer vision with other inputs such as audio, text, or sensor data to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the environment. This is particularly important in applications like robotics and augmented reality.
Synthetic data and AI-driven data augmentation are also gaining traction as a way to train computer vision systems more effectively, especially in environments where real-world data is scarce or hard to annotate.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advancements, the AI in computer vision industry faces several challenges. Data privacy is a major concern, especially in surveillance and facial recognition applications. Ethical use and bias in training data can lead to inaccuracies or discriminatory outcomes.
Another hurdle is the demand for computational resources. Training deep learning models for computer vision requires powerful GPUs and large datasets, which may not be accessible to all organizations. Moreover, explainability remains an issue—understanding how and why a model made a specific decision is often difficult, which can hinder adoption in critical applications like healthcare or law enforcement.
The Future Outlook
The AI in computer vision market is projected to grow exponentially in the coming years, with increasing investment in AI hardware, edge computing, and industry-specific solutions. As AI models become more efficient and easier to deploy, we can expect to see more real-world applications across sectors.
The future of computer vision is not just about recognizing what is seen, but understanding the context, behavior, and intent behind visual data. This shift from recognition to interpretation will open the door to even more powerful and intuitive technologies—ultimately enabling machines to see, think, and act more like humans.
Related Reports @
Semiconductor and Electronics Market Research Reports
