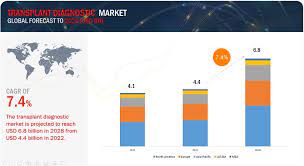
Transplant Diagnostics Market in terms of revenue was estimated to be worth $4.4 billion in 2022 and is poised to reach $6.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 7.4% from 2022 to 2028 according to a new report by MarketsandMarkets™. Organ transplants have gradually improved over the past 20 years and typically produce excellent results in children and young adults. However, the proportion of elderly transplant patients with comorbidities is increasing, posing a greater challenge. When compared to dialysis, renal transplants increase patient survival, and patients with liver, heart, or lung diseases that are incurable must receive life-saving transplants. The activity of solid organ transplant programmes has been steadily increasing, but it still falls short of global needs and varies greatly between nations. Transplanting solid organs is crucial for advanced and established medical systems.
Download an Illustrative overview
Key Drivers of Market Growth
Technological Advancements: Advancements in molecular diagnostics and next-generation sequencing (NGS) are revolutionizing the field of transplant diagnostics. These technologies provide precise and rapid detection of donor-recipient compatibility, significantly improving transplant outcomes.
Rising Number of Organ Transplants: The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, such as end-stage renal disease, liver cirrhosis, and heart failure, has led to a surge in organ transplant procedures. According to the Global Observatory on Donation and Transplantation (GODT), approximately 153,863 organ transplants were performed worldwide, a number that continues to grow annually.
Improved Awareness and Screening: There is a growing awareness about the importance of thorough pre-transplant screening to prevent transplant rejection and complications. This has led to a higher demand for advanced diagnostic tests that ensure better matching of donors and recipients.
Market Segmentation
The transplant diagnostics market is segmented based on technology, product and service, application, and region.
By Technology:
- Molecular Assay Technologies
- PCR-based Assays
- Sequencing-based Assays
- Non-molecular Assay Technologies
By Product and Service:
- Instruments
- Reagents & Consumables
- Software & Services
By Application:
- Diagnostic Applications
- Pre-transplantation Diagnostics
- Post-transplantation Diagnostics
- Research Applications
Regional Insights
North America: North America holds the largest share of the transplant diagnostics market, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and a large number of transplant procedures performed in the region. The United States, in particular, is a key market due to the presence of major players and extensive research activities.
Europe: Europe is the second-largest market, with countries like Germany, France, and the UK being major contributors. The region benefits from a robust healthcare system and significant investments in research and development.
Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period. Factors such as increasing healthcare expenditure, improving healthcare infrastructure, and a growing patient pool contribute to this growth. Countries like China, India, and Japan are leading the charge in this region.
Competitive Landscape
The transplant diagnostics market is highly competitive, with several key players driving innovation and growth. Major companies include Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, and Qiagen N.V. These companies are focusing on strategic collaborations, mergers and acquisitions, and product launches to strengthen their market position.
Conclusion
The transplant diagnostics market is poised for substantial growth, reaching an estimated $6.8 billion by 2028. Technological advancements, increasing organ transplant procedures, and rising awareness about the importance of diagnostics are key factors driving this expansion. As the market evolves, continued innovation and strategic initiatives by key players will be crucial in shaping its future landscape.
Transplant Diagnostics Market – Report Highlights:
- The study consists of the average selling price (ASP) analysis for different products in the Transplant Diagnostic market.
- The research study comprises the patent analysis of technologies/solutions used in the Transplant Diagnostic market
- The new market study consists of the trends/disruptions impacting customers’ businesses.
- The new market study consists of information on key conferences and events in 2022–2028.
- The new market study consists of the region-wise regulatory landscape.
- The new market study provides details of the strategies of the top 5 players operating in the market.
- The competitive landscape chapter has been updated with the market evaluation matrix. The competitive landscape also includes the market share analysis of major global players (as of 2021), updated competitive leadership mapping, and competitive situations and trends.
- The new market study comprises 25 players. These companies have emerged as key market players in recent years due to their products and various strategic investments undertaken in the transplant diagnostic market.
