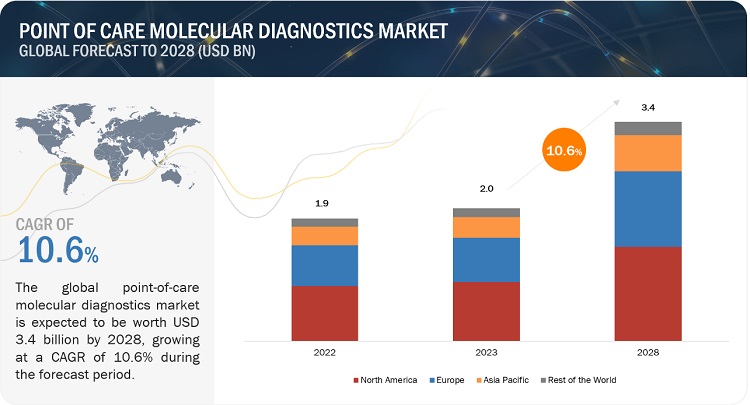
The global point of care molecular diagnostics market was valued at $2.0 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $3.4 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.6% from 2023 to 2028. This comprehensive analysis covers industry trends, detailed pricing analysis, patent insights, conference and webinar information, key stakeholders, and market purchasing dynamics.
Market Drivers
Rising Incidence of Infectious Diseases and Chronic Conditions: The market is primarily driven by the increasing prevalence of infectious diseases and both acute and chronic conditions. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on enhancing healthcare facilities and infrastructure.
Preventive Medicine: There is a rising inclination towards preventive medicine, which is expected to further boost demand for point-of-care molecular diagnostics during the forecast period.
Market Restraints
Uncertain Reimbursement Situations: Market growth is hindered by inadequate reimbursement policies. Diagnostic companies face challenges in securing payments from Medicare and private insurers for their tests. In the US, some tests lack specific Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) codes and are billed using unlisted codes. This has led to jurisdiction-specific payment amounts determined by Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs). Furthermore, Medicare does not currently cover genetic testing for individuals without a personal history of cancer, negatively impacting the market.
Lack of High-Complexity Testing Facilities: The expansion of the market is further constrained by a shortage of facilities capable of performing high-complexity POC molecular diagnostics testing.
Market Opportunities
Emerging Markets: Significant growth opportunities exist in emerging economies like India, South Korea, Brazil, and Mexico. Factors such as relatively low regulatory barriers, advancements in healthcare infrastructure, increasing patient populations, rising incidence of infectious diseases, and higher healthcare expenditure drive these opportunities. Moreover, regulatory policies in some of these countries are more flexible and business-friendly compared to developed nations.
Market Challenges
Alternative Technologies: The development of alternative technologies, such as those used in COVID-19 testing, poses a potential challenge to market growth. Serological and antigen tests, often referred to as rapid tests, provide results within 15 minutes and are cheaper to produce than molecular tests due to their simpler design. The advent of these alternatives could hinder the growth of the point-of-care molecular diagnostics market.
Market Ecosystem
Leading companies in the point of care molecular diagnostics market include Abbott Laboratories (US), F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. (Switzerland), bioMérieux SA (France), Danaher Corporation (US), and QIAGEN N.V. (Netherlands). These companies have strong financial stability, state-of-the-art technologies, diversified product portfolios, and extensive global sales and marketing networks.
Market Segmentation
By Product & Service:
- Assays & Kits
- Instruments & Analyzers
- Software & Services
By Technology:
- RT-PCR
- INAAT
- Other Technologies
By Application:
- Respiratory Diseases
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases
- Hospital-acquired Infections
- Cancer
- Hepatitis
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Other Applications
By End User:
- Physicians’ Offices
- Hospitals & ICUs
- Research Institutes
- Other End Users
By Region:
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Rest of Europe (RoE)
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific (RoAPAC)
- Rest of the World (RoW)
Key Insights and Future Outlook
In 2022, the assays & kits segment held the largest market share, driven by frequent purchases due to recurrent usage. The RT-PCR technology segment also dominated the market, known for its ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and quick turnaround time. Physicians’ offices were the leading end-users, leveraging the quick results provided by point-of-care molecular assays and kits.
Regional Insights: North America accounted for the largest market share in 2022, propelled by a high burden of infectious diseases and cancers, a well-developed healthcare infrastructure, and the adoption of advanced testing technologies.
Recent Developments
- April 2023: QIAGEN N.V. launched QIAstat-Dx in Japan with a respiratory panel for syndromic testing.
- June 2022: Biocartis NV introduced the Rapid CE-marked IVD Idylla GeneFusion Panel for swift lung cancer treatment decisions.
- May 2022: bioMérieux SA received De Novo FDA Authorization for its BIOFIRE Joint Infection (JI) Panel.
- September 2021: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. acquired TIB Molbiol, expanding its PCR test portfolio with a wide range of assays for infectious diseases.
Conclusion
The point of care molecular diagnostics market is set for significant growth driven by the increasing prevalence of infectious diseases and cancer, the rise of preventive medicine, and the expansion of healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets. However, challenges such as uncertain reimbursement situations and the emergence of alternative technologies need to be addressed to fully capitalize on the market’s potential.
