The LiDAR market Insights is rapidly evolving as industries seek precise, real-time spatial data to enhance operations, improve safety, and streamline decision-making. LiDAR technology, which uses laser pulses to measure distances and generate high-resolution 3D models, has become a critical tool in industrial applications ranging from surveying and asset management to autonomous navigation. Understanding the market through the lens of installation, type, and range provides valuable insights into current trends and future opportunities.
Market Drivers and Growth Outlook
The LiDAR market is witnessing accelerated growth, driven by digital transformation across industries. Rising demand for automation, the adoption of smart infrastructure, and the increasing need for accurate geographic and structural data are key growth factors. Industries such as construction, mining, utilities, and transportation are integrating LiDAR solutions to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve operational safety.
Advancements in LiDAR technology, falling hardware costs, and growing awareness of its benefits are expected to sustain this growth over the next decade. The market is poised for further expansion as LiDAR systems become more compact, accurate, and affordable for industrial applications.
Installation Segments: Airborne vs. Ground-Based
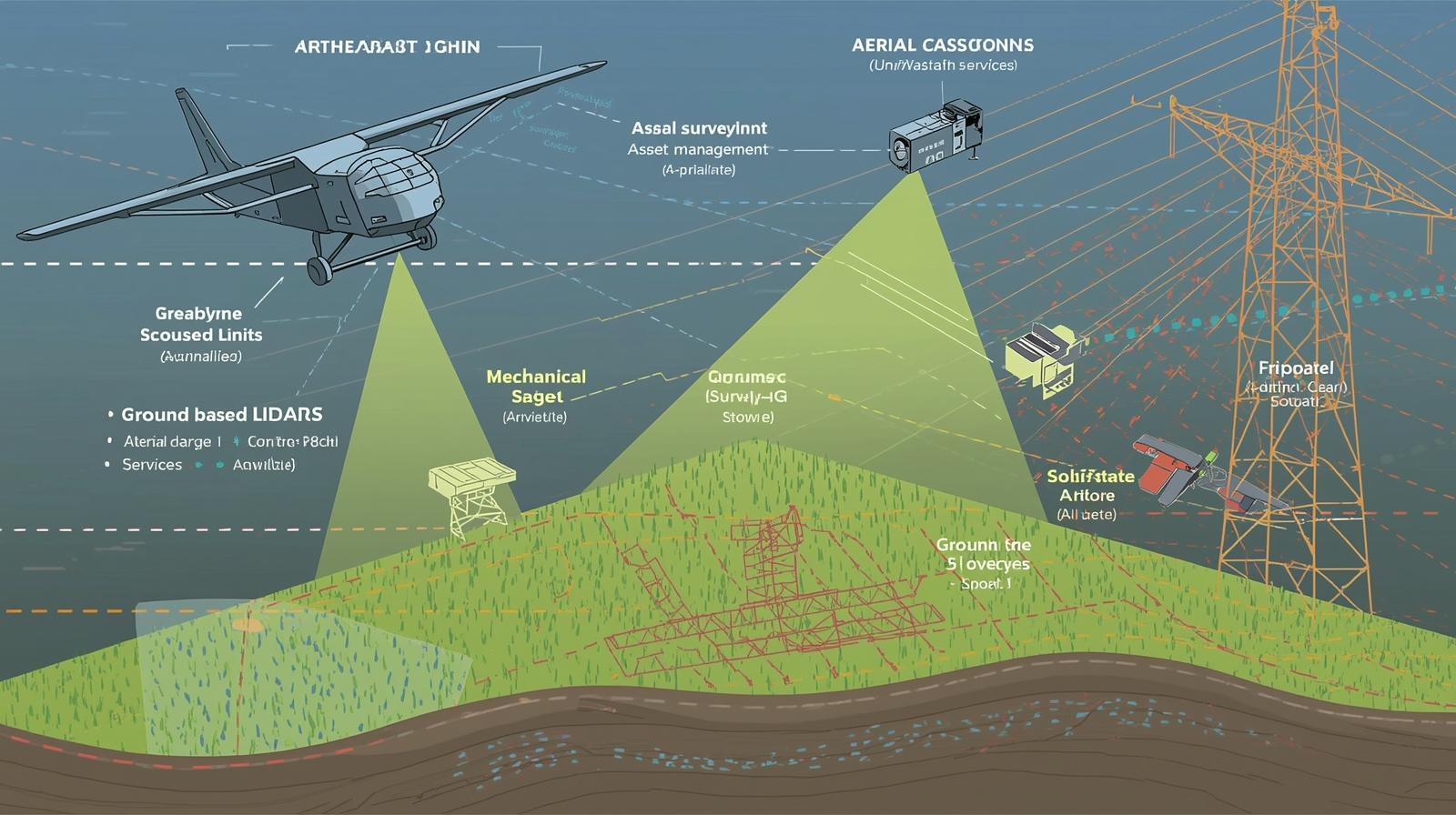
Airborne LiDAR is mounted on aircraft, drones, or helicopters to capture large-scale topographic data. This installation type is ideal for mapping extensive areas, monitoring pipelines, assessing forestry or environmental resources, and supporting infrastructure planning. Its strength lies in quickly covering vast terrains while providing high-resolution data, making it invaluable for industries that require large-area surveys.
Ground-based LiDAR, in contrast, is installed on tripods, vehicles, or mobile robotic platforms. It excels in detailed, close-range applications such as building information modeling (BIM), industrial plant inspection, mining site monitoring, and asset management. By capturing dense point clouds with fine geometric accuracy, ground-based LiDAR enables precise measurements in environments where airborne solutions may lack resolution or accessibility.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=1261
Type Segments: Mechanical vs. Solid-State
LiDAR systems are primarily divided into mechanical and solid-state types:
-
Mechanical LiDAR employs spinning mirrors or rotating components to scan the environment. This design allows wide coverage and long-range detection, making it suitable for large-scale industrial surveys and complex mapping projects. Its established reliability has made it the traditional choice for many industrial applications.
-
Solid-state LiDAR eliminates moving parts, using electronic beam steering through MEMS or optical phased arrays. Solid-state LiDAR is smaller, lighter, and more robust, offering lower maintenance and cost. It is increasingly adopted in robotics, automated material handling, and other industrial environments where compact and durable systems are preferred.
Both types complement each other, with mechanical LiDAR serving applications requiring broader coverage and solid-state LiDAR addressing tasks demanding compactness and integration flexibility.
Range Segments: Short, Medium, and Long
The range of LiDAR systems is another defining factor in their industrial applications:
-
Short-range LiDAR (<200 m) is optimized for close-proximity operations such as warehouse automation, safety monitoring, and indoor robotics. High-resolution short-range scanning allows precise navigation and object detection in confined environments.
-
Medium-range LiDAR (200–500 m) is suitable for industrial sites, construction projects, and mid-range surveying. It balances coverage and accuracy, providing detailed mapping without the need for extensive installation.
-
Long-range LiDAR (>500 m) is essential for large-scale infrastructure monitoring, environmental mapping, and aerial surveys. Long-range systems allow industries to monitor extensive areas with minimal field deployment, supporting decision-making in energy, transportation, and environmental sectors.
Key Industrial Applications
The LiDAR market serves diverse industrial applications:
-
Aerial Surveying: Airborne LiDAR provides accurate terrain mapping, corridor monitoring, and infrastructure planning, reducing the time and cost associated with manual surveys.
-
Asset Management: Ground-based LiDAR assists industries in tracking equipment, assessing structural integrity, and optimizing maintenance schedules.
-
GIS Services: LiDAR enriches geographic datasets, offering precise elevation and spatial information for smarter planning and analysis.
-
Industrial Surveying: Detailed 3D mapping enables efficient construction, mining, and plant management, ensuring safety and accuracy in complex environments.
These applications highlight LiDAR’s ability to transform data collection, analysis, and operational decision-making across multiple industries.
Technological Trends and Future Outlook
Emerging trends in the LiDAR market include AI-driven data analytics, cloud-based processing, and tighter integration with autonomous platforms. Solid-state LiDAR is gaining traction due to lower costs, smaller form factors, and minimal maintenance requirements. Coupled with advancements in sensors, processors, and display technologies, LiDAR systems are becoming more intelligent, versatile, and accessible.
Looking forward, the LiDAR market is expected to expand rapidly across industrial applications. Increased automation, smart infrastructure projects, and growing adoption in emerging markets will continue to fuel demand. The combination of mechanical and solid-state technologies, along with short, medium, and long-range systems, ensures that LiDAR remains a cornerstone of modern industrial operations.
The LiDAR market is at the forefront of industrial innovation, delivering precise, high-resolution spatial data across airborne and ground-based installations, mechanical and solid-state systems, and varying range capabilities. Its ability to improve efficiency, safety, and decision-making positions LiDAR as a critical technology for industries embracing digital transformation. As adoption grows, LiDAR will continue to redefine industrial surveying, asset management, GIS, and beyond, shaping the future of intelligent operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – LiDAR Market Insights
1. What is the LiDAR market?
The LiDAR market involves technologies that use laser light to measure distances and generate high-resolution 3D maps. It includes hardware, software, and services applied in industrial surveying, asset management, GIS, and automation.
2. What are the main types of LiDAR systems?
The two primary types are:
-
Mechanical LiDAR: Uses spinning components for scanning, ideal for long-range and large-area industrial applications.
-
Solid-state LiDAR: Uses electronic beam steering, offering compact size, durability, and suitability for robotics, automation, and embedded industrial applications.
3. How is the LiDAR market segmented by installation?
-
Airborne LiDAR: Mounted on drones, helicopters, or airplanes for large-scale mapping, topography, and corridor monitoring.
-
Ground-based LiDAR: Installed on vehicles, tripods, or robots for detailed site surveys, asset inspection, and industrial plant monitoring.
4. What role does range play in LiDAR applications?
LiDAR systems are classified by range:
-
Short-range (<200 m): For close-proximity operations like warehouse automation and indoor robotics.
-
Medium-range (200–500 m): Ideal for industrial sites, construction, and mid-scale surveys.
-
Long-range (>500 m): Used in infrastructure monitoring, environmental mapping, and large-area surveys.
5. Which industrial applications are driving the LiDAR market?
Key applications include:
-
Aerial surveying and topographic mapping
-
Asset management and structural monitoring
-
GIS services and spatial data analytics
-
Ground-based industrial surveying for construction, mining, and plant management
