The conversation around 3D printing has dramatically evolved. Once celebrated primarily for its rapid prototyping capabilities, the technology is now a cornerstone of full scale production and radical innovation. This shift marks a significant milestone in industrial evolution. We are witnessing a move from creating simple models to manufacturing functional end use parts. The landscape of additive manufacturing is expanding at an unprecedented pace. This article will explore the most exciting emerging applications in the 3D printing industry. These advancements are reshaping sectors from healthcare to aerospace in profound ways.

The Foundational Shift from Prototyping to Production
The initial appeal of 3D printing lay in its ability to create physical models directly from digital designs. This revolutionized the design verification process for engineers and designers across the globe. It allowed for rapid iteration and significantly reduced the time from concept to tangible object. However, the true potential of additive manufacturing was always greater than just prototyping. Advances in materials science, printer precision, and software algorithms have enabled this critical transition. Today, industries are confidently using 3D printing for manufacturing robust, final product components. This foundational shift is the bedrock upon which all modern applications are built, unlocking new possibilities.
Revolutionizing Patient Specific Medical Solutions
Perhaps the most impactful of all emerging applications in the 3D printing industry is found within medicine. The technology enables a level of personalization previously thought impossible. Surgeons now use 3D printed models of a patient’s unique anatomy, such as a heart or a complex bone fracture, to meticulously plan surgeries. This practice leads to shorter operation times and improved patient outcomes. The field of bioprinting, while still in its relative infancy, aims to print living tissues using bio inks composed of human cells. This research holds the promise of future organ transplants without donor waiting lists, a truly revolutionary concept.
The Rise of Customized Dental and Orthopedic Implants
In dentistry and orthopedics, 3D printing is becoming the standard of care for creating custom implants. Unlike mass produced implants, 3D printed versions are designed from patient specific CT scans. This ensures a perfect anatomical fit, which is crucial for long term success and patient comfort. Dental labs can produce crowns, bridges, and even full dentures with incredible speed and accuracy. In orthopedics, titanium alloy hip and knee implants can be fabricated with porous surfaces. These porous structures encourage natural bone ingrowth, securely anchoring the implant within the body for a more stable and lasting solution.
Pioneering the Future of Pharmaceutical Development
The pharmaceutical industry is embracing 3D printing to create a new generation of personalized medicines. A significant breakthrough is the ability to fabricate polypills. These are single tablets that contain multiple medications with different release profiles. This technology can precisely control the dosage and timing of drug delivery within one pill. This innovation is particularly beneficial for patients managing chronic conditions who need to take several medications daily. It can greatly improve medication adherence and treatment efficacy. The potential for tailoring drug dosage forms to individual patient needs represents a major step forward in pharmacotherapy.
Transforming the Aerospace and Automotive Sectors
The aerospace and automotive industries were among the first to adopt additive manufacturing for high value applications. The driving forces are the compelling benefits of weight reduction and part consolidation. By creating complex, lightweight geometries that are impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing, 3D printing helps reduce fuel consumption and emissions. Engineers can now design a single, intricate component that replaces an assembly of multiple parts. This consolidation simplifies supply chains, reduces potential failure points, and enhances overall system reliability. These sectors continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with advanced metals and polymers.
Building the Future with Large Scale Construction Printing
The concept of 3D printing entire buildings is no longer science fiction but a tangible reality. Construction scale 3D printing involves using massive gantry systems to extrude concrete or other specialized materials layer by layer. This method offers the potential to build homes and structures faster, with less waste, and at a lower cost than conventional methods. It also allows for architecturally unique and complex designs that would be economically unfeasible otherwise. This technology holds particular promise for rapid disaster relief housing and addressing affordable housing shortages in various parts of the world, demonstrating significant social impact.
Innovations in the Food and Culinary Arts Industry
The emerging applications in the 3D printing industry are even making their way into our kitchens. Food 3D printing is a novel technology that can create intricate edible designs, personalize nutrition, and explore new food textures. Chefs in high end restaurants use it to produce decorative elements that would be incredibly time consuming to craft by hand. On a more functional level, the technology can be used to create meals for elderly individuals with specific nutritional needs or swallowing difficulties. The puree like food can be printed into appealing, familiar shapes, which can help improve appetite and quality of life.
Sustainable Manufacturing and Circular Economy Models
Sustainability is a critical driver for many new technologies, and 3D printing offers distinct advantages. It is inherently an additive process, meaning it adds material only where needed, significantly reducing waste compared to subtractive methods like machining. Furthermore, the technology promotes a circular economy by facilitating local production, which cuts down on transportation related carbon emissions. Companies are also increasingly using recycled plastics and bio based polymers as printing materials. This focus on sustainable practices is making additive manufacturing an environmentally conscious choice for forward thinking manufacturers who are committed to reducing their ecological footprint.
The Critical Role of Advanced Materials Development
The expansion of emerging applications in the 3D printing industry is intrinsically linked to the development of new materials. The capabilities of any 3D printer are defined by the materials it can process. Researchers are constantly innovating, creating advanced polymers with high heat resistance, composite materials infused with carbon fiber for added strength, and flexible resins that mimic the properties of rubber. The list of printable materials now includes metals, ceramics, sand, and even wood based composites. Each new material opens the door to a new set of applications, allowing 3D printing to solve increasingly complex engineering and design challenges across different sectors.
Democratizing Manufacturing Through Accessible Tools
3D printing technology has become remarkably accessible to small businesses, entrepreneurs, and individual makers. Desktop 3D printers are now affordable and user friendly, empowering a new wave of innovation at a grassroots level. This democratization allows inventors to prototype ideas without large capital investment. Artists can create previously impossible sculptures and artworks. Educators use these printers to bring concepts to life in the classroom. This widespread accessibility is fostering a culture of creativity and small scale manufacturing. It is fueling a maker movement that is contributing significantly to the overall growth and diversity of applications within the industry.
The global 3D Printing Market was valued at USD 15.39 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 16.16 billion in 2025 to USD 35.79 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 17.2% during the forecast period.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=1276
Overcoming Challenges for Widespread Adoption
Despite the rapid progress, several challenges must be addressed for the broader adoption of these emerging applications in the 3D printing industry. Speed of production, while improving, is still a limitation for very high volume manufacturing. The cost of industrial grade machines and specialized materials can be prohibitive for some businesses. There is also a need for standardized processes and quality control certifications, especially in highly regulated fields like aerospace and medicine. Furthermore, there is a growing skills gap, creating a demand for professionals trained in design for additive manufacturing, a specialty that differs significantly from traditional engineering principles.
Envisioning the Future Landscape of Additive Manufacturing
The future of 3D printing is incredibly promising, with research pushing the boundaries even further. We can anticipate the rise of multi material printing, where a single object can be printed with integrated electronics, soft and hard materials simultaneously. Artificial intelligence will be integrated to optimize designs for weight and strength and to monitor the printing process in real time for defects. The scale of printing will continue to expand in both directions, from micro scale medical devices to entire architectural structures. These advancements will further blur the line between the digital and physical worlds, unlocking unprecedented creative and industrial potential.
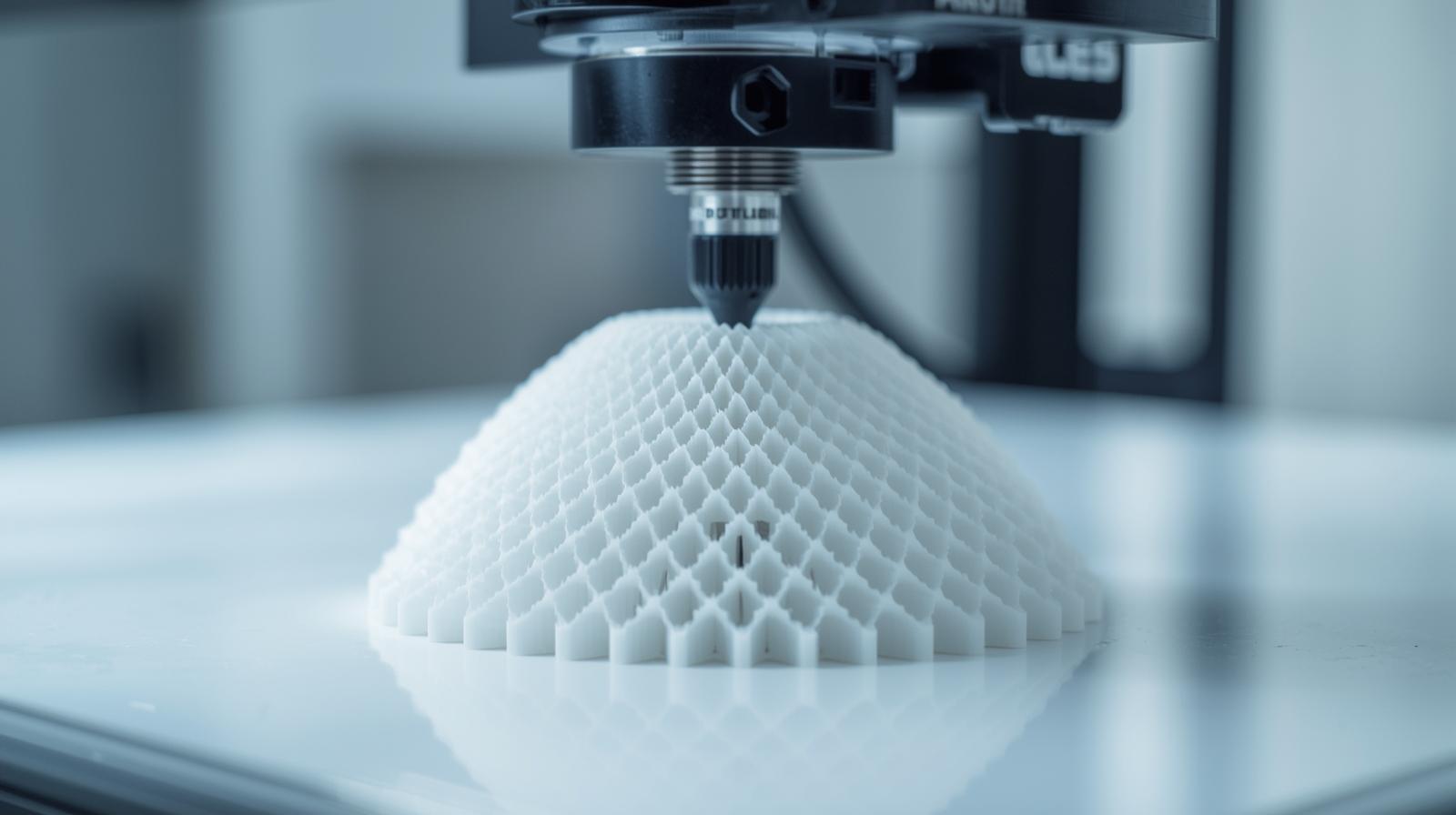
An Industry Redefining Possibility
In conclusion, the narrative of 3D printing has been completely rewritten. It is no longer a niche tool for prototyping but a powerful, versatile manufacturing technology that is reshaping our world. The emerging applications in the 3D printing industry, from life saving medical implants to sustainable construction methods, demonstrate its profound impact. As materials diversify, printers become faster, and software becomes more intelligent, this impact will only deepen. The industry is poised for continued exponential growth, fundamentally changing how we design, produce, and interact with the physical objects around us, redefining the very notion of what is possible.
Explore In-Depth Semiconductor & Electronics Market Research:
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/semiconductorand-electonics-market-research-87.html
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the most promising emerging applications in the 3D printing industry today?
The most promising applications are in personalized healthcare, including surgical guides and custom implants, followed by aerospace component manufacturing, construction printing, and the development of personalized pharmaceuticals.
Q2: How is 3D printing contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices?
3D printing promotes sustainability by being an additive process that generates minimal waste, enabling local production to reduce transportation emissions, and facilitating the use of recycled and bio based materials.
Q3: Is 3D printing capable of mass production, or is it only for one off items?
While traditionally used for prototypes and low volume parts, 3D printing is increasingly used for mass production, especially for complex, lightweight parts in industries like aerospace and for customized products like hearing aids.
Q4: What are the main materials used in modern industrial 3D printing?
Industrial 3D printing uses a wide range of materials, including various plastics like ABS and Nylon, photopolymer resins, metal powders such as titanium and aluminum, and advanced composites like carbon fiber reinforced materials.
See The Latest Semiconductor Reports:
Proximity Sensor Market Size, Share & Trends : https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/proximity-sensor-market-36281914.html
Terahertz Technology Market Size, Share & Trends : https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/terahertz-technology-market-71182197.html
Cryocooler Market Size, Share & Trends : https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/cryocooler-market-247727537.html
Time-Sensitive Networking Market Size, Share & Trends : https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/time-sensitive-networking-market-215000493.html
Actuators Market Size, Share & Trends : https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/global-actuators-market-59465451.html
Battery Technology Market Size, Share & Trends: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/battery-technology-market-253343109.html
