The global humanoid robot market trends is experiencing rapid growth as advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and automation converge to redefine human-machine interaction. These life-like machines are moving beyond research labs and science fiction into real-world roles across sectors such as healthcare, education, retail, and defense. Key technological developments in robotic locomotion, sensor integration, and actuator design are enabling humanoid robots to become smarter, more mobile, and more responsive to human needs.
The Rise of Biped and Wheel-Drive Humanoid Robots
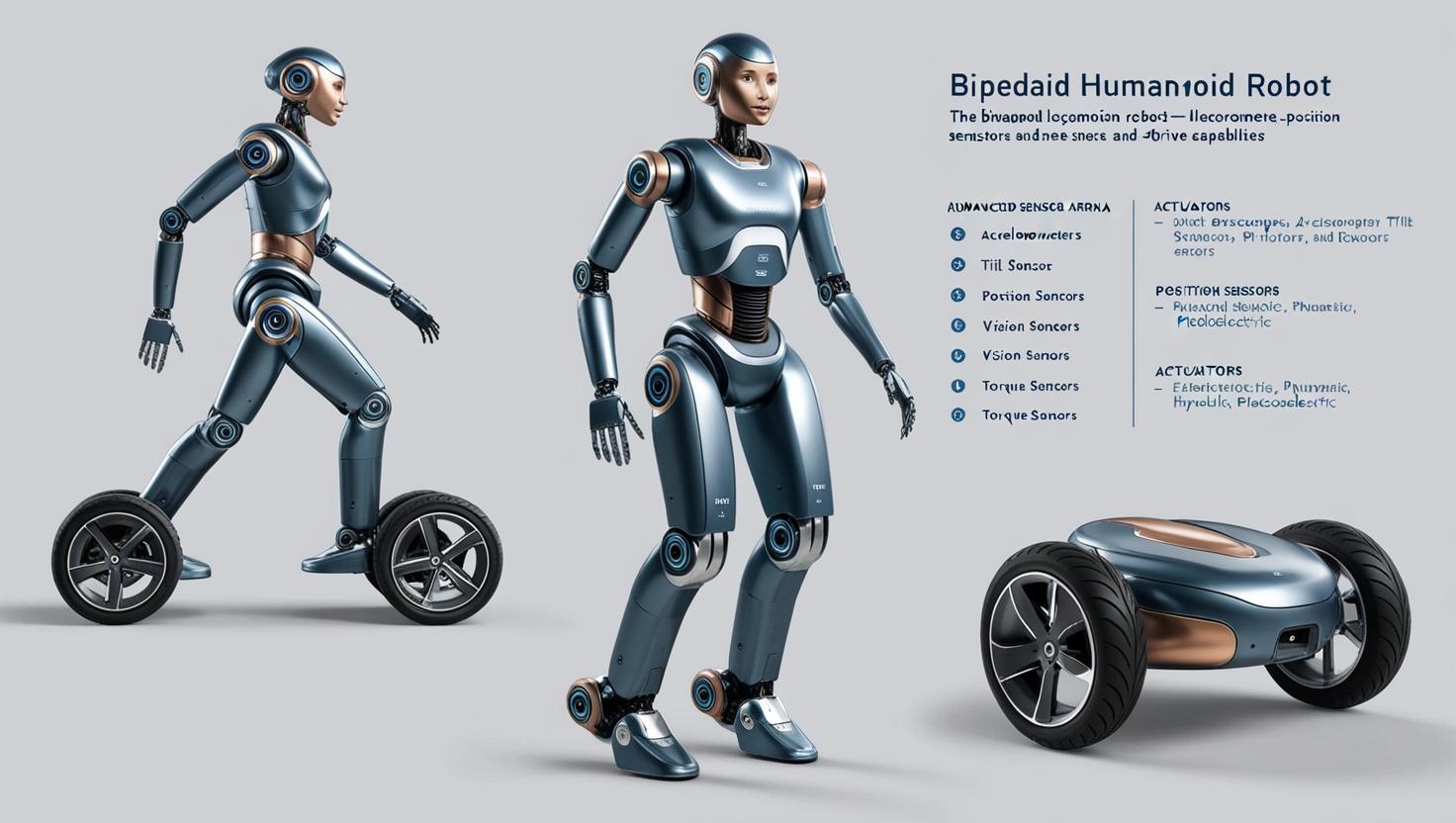
Two primary locomotion types are leading the charge in humanoid robotics: biped robots and wheel-drive robots.
Biped humanoid robots, designed to replicate human walking and movement, are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Their ability to navigate uneven terrain and mimic human motion makes them ideal for environments like healthcare facilities, disaster response zones, and entertainment venues. Companies like Boston Dynamics and Agility Robotics are pushing boundaries in biped mobility with robots that walk, run, and balance with impressive agility.
On the other hand, wheel-drive humanoid robots offer simplicity, speed, and stability, making them ideal for customer service applications in retail, airports, and hotels. Their lower cost and easier control system are driving adoption where full-range motion isn’t necessary.
Sensor Technologies Powering Human-Robot Interaction
Sensor technology is a cornerstone of humanoid robot development. These sensors enable robots to perceive their environment, interpret human actions, and respond accurately and safely.
Key sensors include:
-
Gyroscopes and Accelerometers: These help in balance and motion tracking, essential for walking robots.
-
Tilt and Position Sensors: These assist in posture control and spatial orientation.
-
Vision Sensors: Using cameras and image processors, robots can recognize faces, gestures, and objects, crucial for interactive roles.
-
Torque Sensors: Vital for detecting force feedback, ensuring safe human-robot interaction and smooth joint movements.
This fusion of sensor data supports advanced AI models that allow robots to learn from experience, adapt in real-time, and function in dynamic environments.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=99567653
Actuators: Bringing Motion to Mechanical Limbs
The evolution of actuators—devices that convert energy into motion—has been instrumental in enhancing humanoid robot performance. Each type offers specific benefits depending on the robot’s application.
-
Electrical Actuators: Widely used for their precision, efficiency, and controllability. Ideal for lightweight, battery-operated humanoids.
-
Pneumatic Actuators: Provide soft and flexible movement, useful in robots that interact closely with humans or require shock absorption.
-
Hydraulic Actuators: Deliver high force and are used in heavy-duty applications such as exoskeletons or military-grade humanoids.
-
Piezoelectric Actuators: Known for micro-scale motion and precision, making them useful in delicate tasks like surgery or micromanufacturing.
The integration of these actuators with intelligent control systems is giving rise to humanoid robots capable of fluid, life-like movement and responsive actions.
Market Outlook: Rapid Expansion with Diverse Applications
The global humanoid robot market is projected to witness substantial growth over the next decade, driven by:
-
Rising demand for human-assistive robots in healthcare and eldercare
-
Automation in retail and customer service roles for 24/7 engagement
-
Educational robots aiding STEM learning in schools
-
Increased funding and R&D from governments and private tech firms
Asia-Pacific is emerging as a dominant region due to technological leadership from Japan, South Korea, and China. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are seeing growing investment in humanoid robotics for both civilian and military use.
Conclusion: A Future Defined by Collaboration
As humanoid robots continue to evolve, they are no longer tools of convenience—they are becoming collaborators, assistants, and companions. The intersection of AI, robotics, and sensor technology is enabling machines that can learn, adapt, and interact meaningfully with humans. The next frontier in automation is not just about replacing human labor—it’s about enhancing it through intelligent, empathetic, and capable robotic partners.
FAQ
1. Why should investors care about the humanoid robot market?
The humanoid robot market sits at the intersection of AI, automation, and human-machine collaboration—three of the most transformative trends shaping the future of work and service industries. The market is expected to grow significantly, fueled by rapid adoption in healthcare, education, retail, and logistics, offering long-term investment opportunities.
2. What’s the current and projected market size?
The global humanoid robot market is expected to grow from USD 2.92 billion in 2025 to USD 15.26 billion in 2030, with a CAGR of 39.2%. Demand is accelerating as businesses seek scalable solutions for labor-intensive and interactive roles.
3. What technologies make humanoid robots a high-growth area?
Humanoid robots leverage:
-
AI and machine learning for autonomy and adaptive behavior
-
Advanced sensors (vision, position, torque) for human-like perception
-
Actuators (electrical, pneumatic, hydraulic) for fluid movement
-
Natural language processing (NLP) for verbal interaction
These integrated technologies increase both utility and market value, making them attractive for diversified investment across hardware, software, and AI verticals.
4. Which sectors are adopting humanoid robots most aggressively?
-
Healthcare: For elderly care, rehabilitation, and surgery assistance
-
Retail & Hospitality: For customer service and information delivery
-
Education: As teaching aids and engagement tools
-
Logistics & Manufacturing: In roles requiring human-robot collaboration
-
Defense & Research: For field tasks and AI development
These sectors offer recurring revenue models (e.g., robotics-as-a-service) and strong demand tailwinds.
