The global humanoid robot market is undergoing rapid transformation, propelled by breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, robotics hardware, and sensor technology. Once confined to research labs and science fiction, humanoid robots are now making their way into industries such as healthcare, logistics, education, retail, and customer service.
At the heart of this growth is innovation in mobility platforms—especially in bipedal and wheel drive humanoid robots—that are reshaping how robots interact with human environments. As developers refine mobility, balance, perception, and control systems, humanoid robots are becoming more functional, agile, and adaptable to real-world tasks. This expansion is driving increased investments and pushing the market toward a projected valuation of several billion USD by 2030.
Understanding Humanoid Robot Platforms: Biped vs Wheel Drive
Humanoid robots are designed to replicate the form and, to varying degrees, the movement and behavior of the human body. Among the most defining features are their mobility systems, which determine how they navigate the environment.
Bipedal humanoid robots are engineered to walk on two legs, mimicking human locomotion. They are ideal for navigating stairs, uneven surfaces, and tight spaces where wheel-based robots might struggle. However, they require advanced control algorithms, real-time sensor integration, and powerful actuators to maintain balance and stability.
Wheel drive humanoid robots, in contrast, use wheels for movement and typically offer greater stability and energy efficiency. These robots are often preferred for indoor environments such as hospitals, airports, and retail spaces, where speed, safety, and smooth floor surfaces allow them to excel.
The market is seeing demand for both types, with applications tailored to the strengths of each. As a result, manufacturers are developing hybrid models and customizable platforms that meet the needs of specific industries.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=99567653
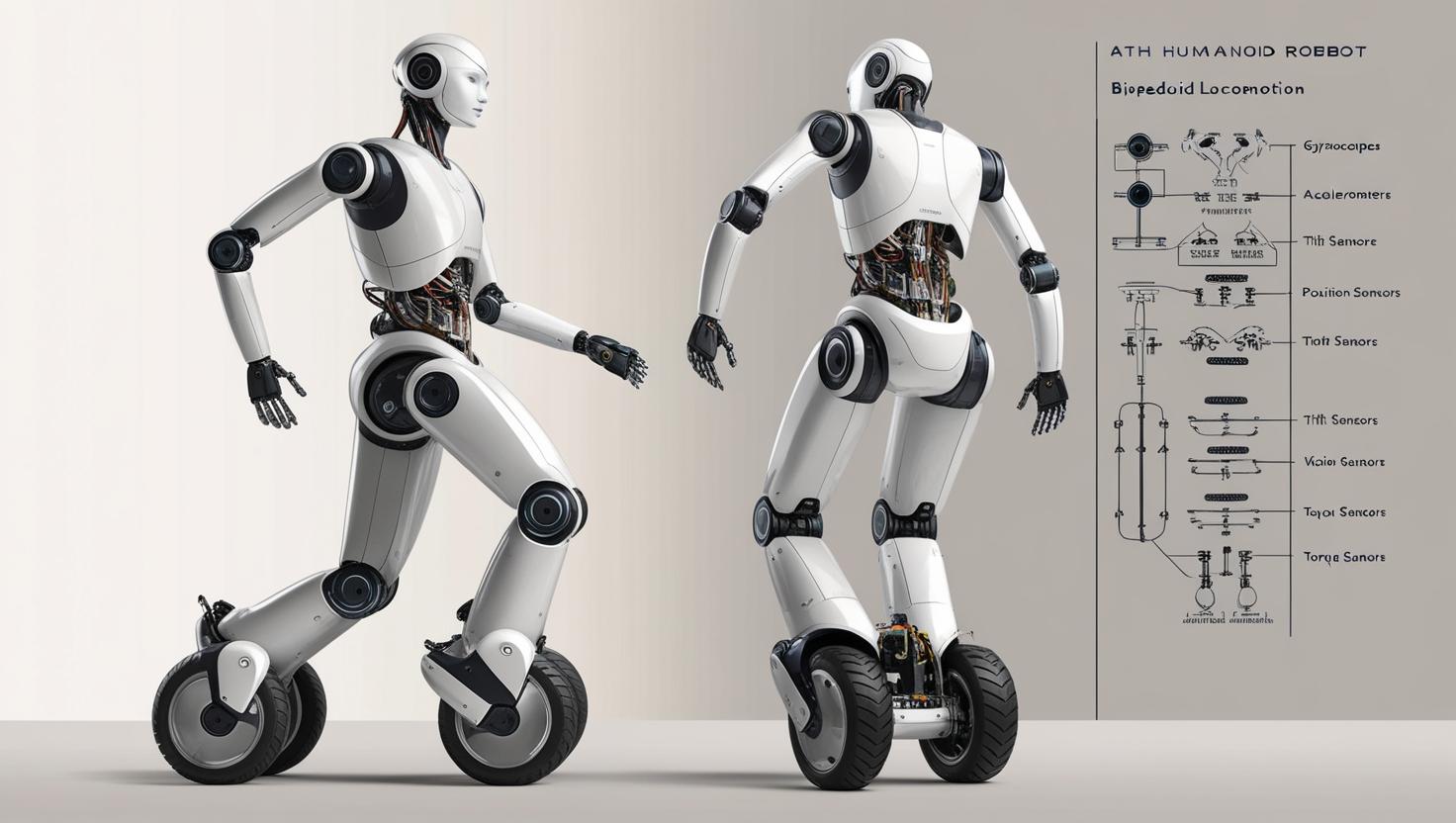
Sensors: The Foundation of Perception and Control
Modern humanoid robots rely on a sophisticated array of sensors to interpret the world around them and respond in real time. These sensors are critical for navigation, interaction, task performance, and safety.
Gyroscopes and accelerometers provide data on orientation and motion, helping robots maintain balance—especially important for biped models. Tilt sensors enhance postural control, ensuring the robot stays upright under dynamic conditions.
Position sensors play a crucial role in joint movement and limb coordination, enabling precise motions and gestures. Vision sensors, such as cameras and LiDAR, allow robots to recognize faces, detect objects, and navigate complex environments.
Torque sensors enable robots to measure force and adjust grip or movement accordingly—vital for tasks involving interaction with humans or delicate objects.
Together, these sensors form a multi-modal feedback system that allows humanoid robots to operate autonomously and safely in human-centric spaces.
Actuators: Powering Human-Like Movement
Actuators are the mechanical muscles of humanoid robots. Innovations in actuation technology have significantly improved the fluidity, precision, and energy efficiency of robotic movement.
Electric actuators dominate the market due to their control precision, responsiveness, and ease of integration. They are commonly used in joints for arms, legs, and fingers, allowing for complex, coordinated movement.
Pneumatic and hydraulic actuators offer higher power density and are sometimes used in larger robots or those performing tasks that require high force, though they can be less precise and more difficult to maintain.
Piezoelectric actuators, though less common, are gaining attention for their small size and high accuracy in micro-motion tasks, making them suitable for facial expressions or medical robotics applications.
Manufacturers are increasingly focused on lightweight, energy-efficient actuators that replicate the range and nuance of human motion while reducing wear and energy consumption.
Key Applications Driving Market Demand
As biped and wheel drive humanoid robots become more capable and affordable, their use cases are expanding across multiple industries.
In healthcare, humanoid robots are assisting with eldercare, rehabilitation, and patient engagement. They can provide medication reminders, guide patients through physical exercises, and offer companionship.
In education, robots are used to teach STEM concepts, interact with students, and support language learning. Their humanoid form makes them engaging and effective in classroom settings.
Retail and hospitality industries are leveraging humanoid robots for customer interaction, product guidance, and concierge services. Their presence enhances brand image while providing consistent service.
Industrial and logistics sectors are exploring humanoid robots for warehouse navigation, material handling, and repetitive assembly-line tasks, especially where human-like dexterity is needed.
Regional Insights and Market Growth
Asia-Pacific leads the global humanoid robot market, particularly driven by innovation hubs in Japan, South Korea, and China. These countries are investing heavily in robotics R&D and deploying humanoid robots in public and commercial spaces.
Europe is a close follower, with strong support from government-funded AI initiatives and robotics programs, especially in Germany and the Nordic countries. North America, led by the U.S., is seeing rapid adoption in education, healthcare, and research applications, thanks to a strong ecosystem of AI and robotics startups.
Emerging markets in the Middle East and Latin America are also beginning to explore humanoid robotics for tourism and public service automation.
Key Players and Innovations
The global market includes established robotics companies, tech giants, and innovative startups. Major players include:
-
Honda Robotics – known for ASIMO, one of the first advanced biped robots.
-
SoftBank Robotics – creators of Pepper and NAO robots, widely used in education and retail.
-
Boston Dynamics – while more focused on quadrupeds, their humanoid robot Atlas showcases advanced bipedal motion.
-
Ubtech Robotics – a leader in consumer humanoid robots and educational robotics solutions.
-
Toyota Research Institute, PAL Robotics, Agility Robotics, and Tesla (with its Optimus project) are also contributing to major advancements.
Companies are prioritizing improvements in AI integration, cloud connectivity, emotional intelligence, and modularity to broaden the use of humanoid robots across both personal and professional domains.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead to 2030, the humanoid robot market is poised for substantial expansion. Continued innovations in bipedal walking algorithms, sensor fusion, natural language processing, and human-robot interaction will unlock new capabilities.
Biped robots are expected to become more agile, navigating stairs and uneven surfaces with ease, while wheel-based models will evolve for ultra-efficient service delivery. Improvements in battery life, cloud control, and safety standards will make humanoid robots viable in environments that were previously off-limits.
As costs decline and capabilities rise, humanoid robots will shift from novelty to necessity—functioning not just as assistants, but as collaborative partners across industries.
The global humanoid robot market is expanding rapidly, driven by technological innovation and a growing range of practical applications. The evolution of biped and wheel drive platforms, supported by advancements in sensors and actuators, is making humanoid robots more capable, intelligent, and useful than ever before. As we move toward 2030, these robots will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of work, education, healthcare, and everyday life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a humanoid robot?
A humanoid robot is a machine designed to resemble the human body in form and function. It typically features a torso, head, arms, and legs (or wheels), and may mimic human behaviors like walking, speaking, or gesturing. Humanoid robots are used in a variety of applications including healthcare, education, customer service, and research.
2. What is the difference between biped and wheel drive humanoid robots?
Biped robots walk on two legs like humans, enabling them to navigate stairs, uneven surfaces, and confined spaces. Wheel drive robots use wheels for mobility, offering greater stability and efficiency on flat, smooth surfaces. Each platform is suited to different use cases depending on the environment and mobility needs.
3. Why is the humanoid robot market growing?
The market is expanding due to advancements in AI, robotics engineering, sensors, and actuators. Increasing demand for automation in service industries, aging populations (especially in Asia and Europe), labor shortages, and growing interest in human-robot interaction are driving adoption across sectors like healthcare, retail, and education.
4. What industries are using humanoid robots today?
Humanoid robots are being adopted in:
-
Healthcare (eldercare, patient monitoring, companionship)
-
Education (interactive learning, STEM teaching)
-
Retail and hospitality (greeting customers, providing information)
-
Logistics and manufacturing (light-duty tasks, safety monitoring)
-
Public services and entertainment
