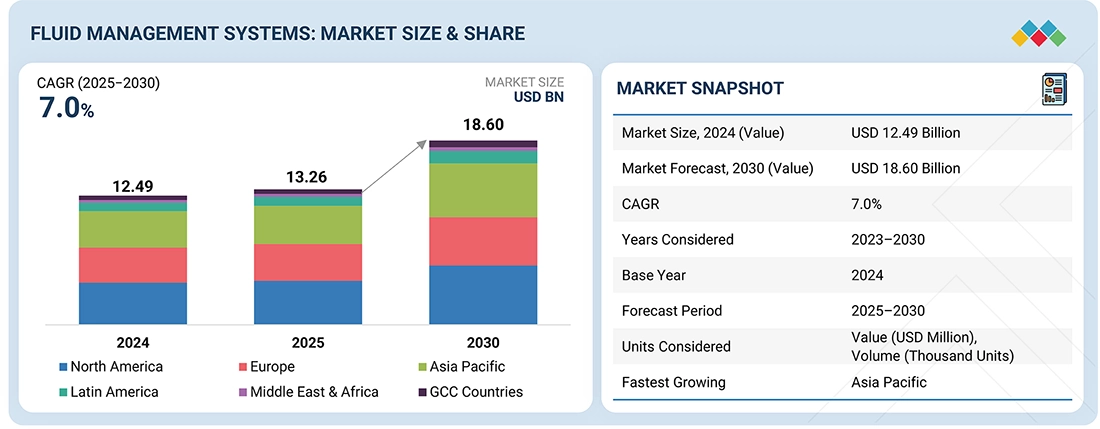
The global Fluid Management Systems (FMS) market, defined as the segment of medical devices and consumables designed to regulate fluid inflow, outflow, and balance during surgical and diagnostic procedures, reached US$12.5 billion in 2024, increased to US$13.3 billion in 2025, and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.0% between 2025 and 2030, attaining US$18.6 billion by 2030.
This growth trajectory is primarily driven by the rising global prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD), urological disorders, and gastrointestinal complications, all of which necessitate precise fluid regulation during treatment. According to the International Society of Nephrology (ISN, 2023), 850 million people worldwide are affected by kidney disease, underscoring the urgent need for dialysis-related consumables and fluid management technologies.
The efficiency of FMS lies in their ability to maintain optimal fluid balance, ensure sterile environments, and reduce operative risks. Integrated and automated systems, such as insufflators, suction-irrigation devices, and fluid warming systems, improve surgical precision, reduce infection rates by up to 30% (CDC, 2023), and shorten recovery periods.
Despite their proven benefits, adoption faces obstacles, particularly due to high device costs, limited awareness in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), and workforce shortages in surgical care providers.
DRIVER: Rising Number of Minimally Invasive Surgeries
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) refers to surgical interventions performed with small incisions using advanced instruments such as endoscopes and laparoscopic tools. MIS is increasingly preferred due to shorter hospital stays, reduced infection rates, and faster recovery, with the global MIS volume expected to rise by 8% annually (OECD, 2024).Advanced fluid management systems—including insufflators, suction units, and irrigation technologies—are indispensable to MIS as they maintain clear visual fields, regulate internal pressure, and ensure accurate fluid replacement.
RESTRAINT: High Cost of Endosurgical Procedures
Endosurgical procedures are minimally invasive operations conducted using endoscopes combined with fluid regulation systems. Costs vary significantly, with average expenditures ranging from USD 713 to USD 6,000 per encounter in the US (Medicare, 2024).High costs, combined with restricted reimbursement schemes in the US and EU and budgetary limits in LMICs, directly impede widespread FMS adoption.
OPPORTUNITY: Untapped Potential in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America represent regions with limited but rapidly growing surgical infrastructure. The WHO (2024) estimates that 143 million additional surgical procedures are required annually, signaling vast unmet demand for fluid regulation technologies.
Manufacturers can reduce costs through localized production, standardized consumables, and public-private partnerships to expand accessibility.
CHALLENGE: Shortage of Surgeons
Surgical workforce shortages reflect the global disparity between patient needs and available trained professionals. Despite a 37% increase in US surgical residents since 2007, the number of practicing surgeons has only grown by 10% (ACS, 2025).Africa alone is projected to face a deficit of 5.6 million surgical care providers by 2030 (Operation Smile, 2025). This workforce bottleneck significantly constrains procedure volumes and, consequently, the deployment of fluid management systems.
Market Segmentation
By Application: Urology & Nephrology
The urology & nephrology segment encompasses medical disciplines targeting kidney disorders, urinary tract diseases, and dialysis treatment. With chronic kidney disease affecting 1 in 10 people worldwide (ISN, 2023), demand for dialysis consumables, suction systems, and irrigation devices remains consistently high. This segment accounted for the largest global FMS market share, primarily due to rising CKD incidence, kidney stones, and prostate surgeries.
By End User: Hospitals
Hospitals represent the largest institutional healthcare providers conducting high volumes of surgical and dialysis procedures. Their advanced infrastructure, capacity to absorb high capital costs, and comprehensive patient inflow position them as the leading adopters of FMS worldwide. Hospitals leverage FMS to optimize procedural safety, streamline operating room efficiency, and minimize surgical fluid imbalance risks.
